39. Combination Sum
tag. array
Given a set of candidate numbers (candidates) (without duplicates) and a target number (target), find all unique combinations in candidates where the candidate numbers sums to target.
The same repeated number may be chosen from candidates unlimited number of times.
Example 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
Input: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
A solution set is:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
|
Solution来源:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/solution/xue-yi-tao-zou-tian-xia-hui-su-suan-fa-by-powcai/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
class Solution:
def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
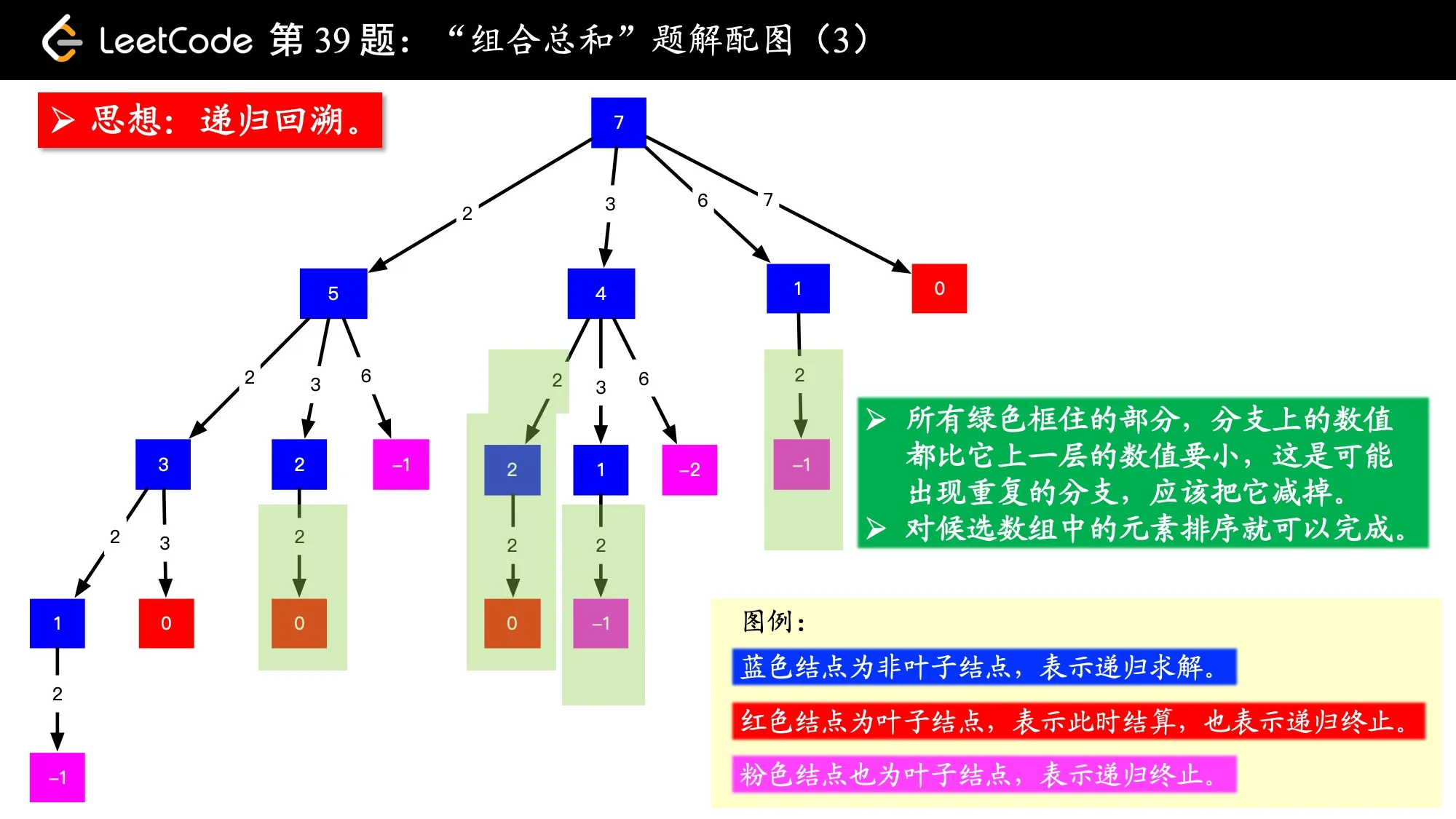
# 剪枝的前提是数组元素排序
# 深度深的边不能比深度浅的边还小
# 要排序的理由:1、前面用过的数后面不能再用;2、下一层边上的数不能小于上一层边上的数。
candidates.sort()
n = len(candidates)
res = []
def backtrack(i, tmp_sum, tmp):
if tmp_sum > target or i == n:
return
if tmp_sum == target:
res.append(tmp)
return
for j in range(i, n):
if tmp_sum + candidates[j] > target:
break
backtrack(j,tmp_sum + candidates[j],tmp+[candidates[j]])
backtrack(0, 0, [])
return res
作者:powcai
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/solution/xue-yi-tao-zou-tian-xia-hui-su-suan-fa-by-powcai/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
|
这道题的图解: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-jian-zhi-python-dai-ma-java-dai-m-2/
输入: candidates = [2, 3, 6, 7],target = 7,所求解集为: [[7], [2, 2, 3]]
![例题图解,这张图画出的结果有 4 个 0,对应的路径是 <code>[[2, 2, 3], [2, 3, 2], [3, 2, 2], [7]]</code> 例题图解,这张图画出的结果有 4 个 0,对应的路径是 <code>[[2, 2, 3], [2, 3, 2], [3, 2, 2], [7]]</code>](/svg/loading/small.min.svg)

补充:事实上,不排序也是可以的,只要保证按顺序读取,也可以通过测试用例。但排序更好一些,这样“剪枝”工作可以更彻底一些。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
class Solution:
def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
size = len(candidates)
if size == 0:
return []
# 剪枝的前提是数组元素排序
# 深度深的边不能比深度浅的边还小
# 要排序的理由:1、前面用过的数后面不能再用;2、下一层边上的数不能小于上一层边上的数。
candidates.sort()
# 在遍历的过程中记录路径,一般而言它是一个栈
path = []
res = []
# 注意要传入 size ,在 range 中, size 取不到
self.__dfs(candidates, 0, size, path, res, target)
return res
def __dfs(self, candidates, begin, size, path, res, target):
# 先写递归终止的情况
if target == 0:
# Python 中可变对象是引用传递,因此需要将当前 path 里的值拷贝出来
# 或者使用 path.copy()
res.append(path[:])
for index in range(begin, size):
residue = target - candidates[index]
// “剪枝”操作,不必递归到下一层,并且后面的分支也不必执行
if residue < 0:
break
path.append(candidates[index])
# 因为下一层不能比上一层还小,起始索引还从 index 开始
self.__dfs(candidates, index, size, path, res, residue)
path.pop()
作者:liweiwei1419
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-jian-zhi-python-dai-ma-java-dai-m-2/
|
在力扣讨论区提到这是一道典型的回溯算法题,点击了解回溯算法。
40. Combination Sum II
tag. List
点击展开题目详情
Given a collection of candidate numbers (candidates) and a target number (target), find all unique combinations in candidates where the candidate numbers sums to target.
Each number in candidates may only be used once in the combination.
Note:
- All numbers (including
target) will be positive integers.
- The solution set must not contain duplicate combinations.
Example 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
Input: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
A solution set is:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
|
这道题和上面的第39道题非常相似,不同的是candidates里面的数字只能取一次。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
class Solution:
def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
size = len(candidates)
if size == 0:
return []
candidates.sort()
res = []
self.__dfs(candidates, size, 0, [], target, res)
return res
def __dfs(self, candidates, size, start, path, residue, res):
if residue == 0:
res.append(path[:])
return
for index in range(start, size):
if candidates[index] > residue:
break
# 剪枝的前提是数组升序排序
if index > start and candidates[index - 1] == candidates[index]:
# [1, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 10]
# 0 号索引的 1 ,从后面 6 个元素中搜索
# 1 号索引也是 1 ,从后面 5 个元素(是上面 6 个元素的真子集)中搜索,
# 这种情况显然上面已经包含。
continue
path.append(candidates[index])
# 这里要传入 index + 1,因为当前元素不能被重复使用
# 如果 index + 1 越界,传递到下一个方法中,什么也不执行
self.__dfs(candidates, size, index + 1, path, residue - candidates[index], res)
path.pop()
作者:liweiwei1419
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-ii/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-jian-zhi-python-dai-ma-java-dai-m-3/
|
202. Happy Number
tag. Math
点击展开详情
Write an algorithm to determine if a number is “happy”.
A happy number is a number defined by the following process: Starting with any positive integer, replace the number by the sum of the squares of its digits, and repeat the process until the number equals 1 (where it will stay), or it loops endlessly in a cycle which does not include 1. Those numbers for which this process ends in 1 are happy numbers.
Example:
Input: 19
Output: true
Explanation:
$$
1^2 + 9^2 = 82\
8^2 + 2^2 = 68\
6^2 + 8^2 = 100\
1^2 + 0^2 + 0^2 = 1\
$$
我的Solution:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
class Solution:
def isHappy(self, n: int) -> bool:
cur = str(n)
while True:
tmp = 0
for i in range(len(cur)):
tmp+=int(cur[i])**2
if tmp == 1:
return True
elif tmp == 4 or tmp == 3:
return False
else:
cur = str(tmp)
|
这道题应该算是纯数学题,需要知道的是:是Happy number会回归到1;如果不是Happy number,计算过程中会回归到3或4。这是数学上的证明,但是如果没有这个数学支持的话,应该把这道题理解成,出现循环(即算出之前算过的数)就不是Happy number,代码就是:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
class Solution:
def isHappy(self, n: int) -> bool:
seen = {1}
while n not in seen:
seen.add(n)
n = sum(int(i) ** 2 for i in str(n))
return n == 1
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/happy-number/solution/python-1xing-by-knifezhu-9/
|
![例题图解,这张图画出的结果有 4 个 0,对应的路径是 <code>[[2, 2, 3], [2, 3, 2], [3, 2, 2], [7]]</code> 例题图解,这张图画出的结果有 4 个 0,对应的路径是 <code>[[2, 2, 3], [2, 3, 2], [3, 2, 2], [7]]</code>](https://ae01.alicdn.com/kf/Ha20d1438c73d485e8f5c7009315a0c63K.jpg)