题记
这两天刷了十道链表题,打算做个总结,刚好leetcode也提供了一个系统学习的链接,这里做一个小总结。
双指针技巧
链表题里面双指针、快慢指针还是经常会用的。
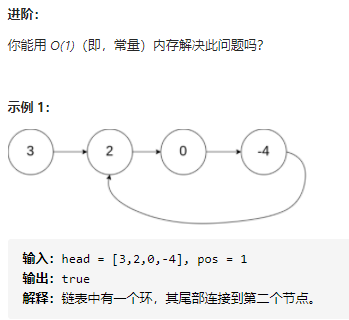
141 环形链表

判断是否有环即可。
只需要知道如果有环,快指针和慢指针的距离会原来越远,但是最后快指针快慢指针一圈,从而相遇。否则,快指针会到达None。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
if not head or not head.next:
return False
slow = head
fast = head.next
while slow != fast:
if not fast or not fast.next:
return False
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return True
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
if not head or head.next is None:
return False
fast, slow = head, head
while True:
if not fast or not fast.next:
return False
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if slow is fast:
return True
|
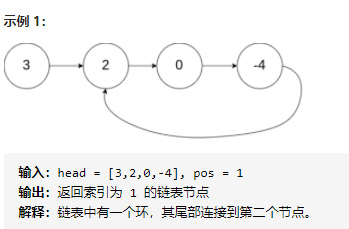
142 环形链表 II

假设a是环外节点数,b是环内节点数(例如上图a=1,b=3)。
-
走a+nb步一定会走到环口(如上图从3走一步,就会到环口2处,此后每走一圈都会回到环扣)。
-
快、慢指针都初始化在head的位置时,第一次slow与fast相遇时,慢指针走了nb步。
证明:a. 快指针的步数f,与慢指针的步数s总有f=2s的关系。 b. 当快慢指针相遇,意味着快指针比慢指针多走了n个环的距离,即f=s+nb。由这两个关系式可得s=nb
-
慢指针如果再走a步就能到环口,但a未知。
-
用双指针,让指针p指向head,此时p走a步到环口、慢指针走a步也到环口,也就是慢指针和p指针相遇的未知就是环口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
fast, slow = head, head
while True:
if not fast or not fast.next:
return None
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if fast is slow:
# 第一次相遇
break
p = head
while p is not slow:
p = p.next
slow = slow.next
return p
|
160 相交链表
这题是个简单题,因为用set集合很容易就写出来了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
s = set()
p = headA
while p:
s.add(p)
p = p.next
p = headB
while p:
if p in s:
return p
else:
p = p.next
return None
|
不过有一个空间复杂度O(1)的双指针方法,而且看到有一个评论非常妙——这个算法也浪漫了吧,错的人迟早会走散,而对的人迟早会相逢!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
p, q = headA, headB
while p!=q:
if p is None:
p = headB #注意不是回到原本A的起点,而是B的起点
q = q.next
elif q is None:
q = headA
p = p.next
else:
p = p.next
q = q.next
return p
|
找到遇见的地方的方式,是各自都完整走过两个list。
经典问题
206 反转链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or head.next is None:
return head
a,b = head, head.next
head.next = None
while b:
c = b.next
b.next = a
a = b
b = c
return a
|
203 移除链表元素
删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
class Solution:
def removeElements(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode:
p = head
while p:
if p.val != val:
break
p = p.next
if not p:
return None
res = p
pre = p
post = p.next
while post:
if post.val != val:
pre = pre.next
else:
pre.next = post.next
post = post.next
return res
|
用一个哑元节点更优雅一点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
class Solution:
def removeElements(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(None)
dummy.next = head
a, b = dummy, head
while b:
if b.val == val:
a.next = b.next
else:
a = a.next
b = b.next
return dummy.next
|
328 奇偶链表
给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起。请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性。
请尝试使用原地算法完成。
1
2
|
输入: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL
输出: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
class Solution:
def oddEvenList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
a, b = head, head.next # a是奇数节点,b是偶数节点
even_start = b # 最后一个奇数节点要指向第一个偶数节点
while b and b.next:
a.next = b.next
b.next = b.next.next
a = a.next # 注意这里的a.next是原本的a.next.next
b = b.next
a.next = even_start
return head
|
234 回文链表
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。返回True/False。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
class Solution:
def get_mid(self, head):
dummy = ListNode(None)
dummy.next = head
slow, fast = dummy, dummy
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return slow
def reverse(self, head):
if not head or not head.next:
return head
a,b = head, head.next
head.next = None
while b:
tmp = b.next
b.next = a
a = b
b = tmp
return a
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
# 1. 找到中心点 (可以用算出链表长度,和快慢指针两个方法)
mid = self.get_mid(head)
# 2. 反转mid之后的所有节点(不包括mid)
mid.next = self.reverse(mid.next)
# 3. 判断是否相等
p = head
q = mid.next
while q:
if p.val != q.val:
return False
else:
p = p.next
q = q.next
return True
|